Common Runoff Issues
How is the runoff calculated?
HydroCAD provides a choice of runoff techniques, including the SCS/NRCS Unit
Hydrograph procedure (aka TR-20), the Santa Barbara Urban Hydrograph (SBUH) and
the Rational method. The runoff method is
selected on the Settings|Calculation screen.
How do I set the rainfall?
The rainfall parameters are specified on the Rainfall
tab of the Settings|Calculation screen.
Please read about rainfall issues.
 How do I change the "Peak Factor"?
How do I change the "Peak Factor"?
The Peak Factor is a characteristic of the Unit Hydrograph
curve, which is selected on the Unit Hydrograph tab of the
Settings|Calculation screen. The widely-used
SCS UH has a peak factor of 484, while the Delmava UH has a PF of 284.
To change the peak factor you must select the appropriate UH. HydroCAD includes
a complete selection of UH tables to suit most applications, or you can create a
custom UH definition. To explore the UH definitions installed on your computer, start HydroCAD and
select View|Unit Hydrograph.
For further details read about
unit hydrographs.
How do I model the rainfall on a pond?
Include the pond's area within one of your subcatchments, or set up a separate subcat
with a Tc of zero and a CN of 98-100. This will produce instantaneous runoff equal to
the precipitation. Starting with HydroCAD 8.5,
you can use one of the new entries in the CN lookup table that allow the water
surface to be reported as pervious or impervious.
Why does the runoff always peak near 12 hours?
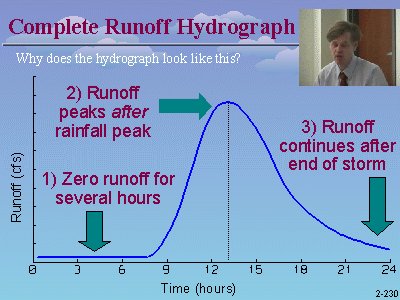 The most common rainfall distributions are synthetic storms, with the
peak rainfall intensity intentionally placed at the mid-point in the storm.
The runoff will always peak at some time after the peak rainfall.
The exact timing depends on the time-of-concentration, but it can never be
earlier than the rainfall peak.
The most common rainfall distributions are synthetic storms, with the
peak rainfall intensity intentionally placed at the mid-point in the storm.
The runoff will always peak at some time after the peak rainfall.
The exact timing depends on the time-of-concentration, but it can never be
earlier than the rainfall peak.
Why don't I get any runoff until about 10 hours?
According to the SCS runoff equation, there will be no runoff until the
rainfall exceeds the initial abstraction, which may not happen until 8-10 hours
into the storm. Until that point, the runoff will be zero. This
effect is most pronounced for low CN values and low rainfall depths, such as
water quality events. For example, a CN value of 80 has an initial
abstraction of 1/2 inch, which isn't satisfied until 11.2 hours for a 2-inch
24-hour Type II storm, and significant runoff does not occur until about 11.7
hours.
Why don't I get any runoff at any time?
With the SCS/NRCS method, the most common reason for getting no runoff is
because the precipitation depth is less than the initial abstraction, resulting
in no runoff. This frequently occurs with a low rainfall depth and/or
curve number. As a cross-check you can evaluate the SCS runoff equation by
hand. Details here.
Using an incorrect time span can also result in no runoff. If the span
ends before the actual runoff begins, no flow will be shown. For
details read about the calculation time span.
 What is the calculation "Time Span"?
What is the calculation "Time Span"?
The time span specifies the timer period over which runoff and routing
calculations will be performed. Using an appropriate time span is
essential to getting meaningful results from your model.
Details here.
Why is the reported runoff depth less than predicted by TR-55?
To match the runoff depth given by the SCS runoff equation, the time span
must include all times at which runoff will occur. To "see" the entire
runoff volume (and the equivalent runoff depth) the time span must end sometime
after the end of the storm. For a 24-hour storm, a span of 0-30
hours will generally include all the runoff. For additional assistance
with comparing runoff results, please see the step-by-step comparison guide.
Why is the peak runoff greater than TR-20 or TR-55?
For small Tc values, the peak runoff may be slightly greater than predicted
by TR-20 or TR-55. This happens because HydroCAD uses a polynomial-based
rainfall distribution which provides better "resolution" than the tabular
rainfall data used in TR-20. If you want to match the TR-20 results (or
just verify the reason for the difference) you can
download a tabular version of the rainfall tables for use with HydroCAD.
But keep in mind that the tabular rainfalls were not intended for use with small
Tc values, and will become less accurate as the Tc value decreases.
If you need further assistance with resolving a runoff difference, please see
the step-by-step comparison guide.
How do I model a snowmelt event?
There is no single approach to modeling snowmelt or rainfall on a snow-pack, nor are
there specific rainfall distributions for these studies. You need to determine
exactly what calculations are appropriate before you attempt to model the situation in
HydroCAD. Here are some of the techniques we commonly see: